A x + By +Cz +D=0.
The normal vector of the plane:
n= Ai+ Bj+ Ck.
If any one of the A, B and C equals to 0,
then the corresponding axis is parallel to the plane.
Let A1x + B1y +C1z +D1=0, and
A2x + B2y +C2z +D2=0 be two given planes. Let n1 and n2 be the normal vectors of these two planes, then the direction vector of the line given by the intersection of the two planes is given by
v=n1 x n2 =
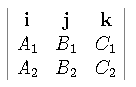 .
.is given by :
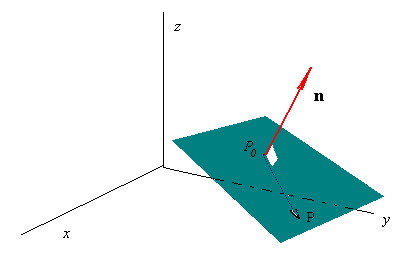
A (x-x0) + B (y-y0) +C (z-z0) +D=0.
P(x0, y0, z0) is a point in the plane with the
normal vector n = Ai+ Bj+ Ck.
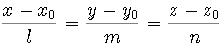 ,
where
,
where
P(x0, y0, z0) is a point in the line, and
v = l i+ m j+ n k. is the direction vector of the line.
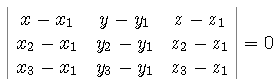 ,
,
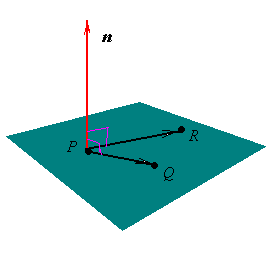
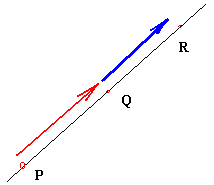
where P(x1, y1, z1), Q(x2, y2, z2) and
R(x3, y3, z3) are 3 points lying in the plane.
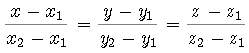 ,
,
where P(x1, y1, z1), Q(x2, y2, z2) are
2 points in the line.
x =x0+l t, y=y0+m t, z=z0+n t,
where P0(x0, y0, z0) is a point in the line, and v = l i+ m j+ n k. is the direction vector of the line.
In vector form, OP(t)= OP0+tv, t is real.
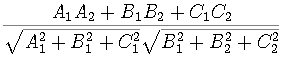 .
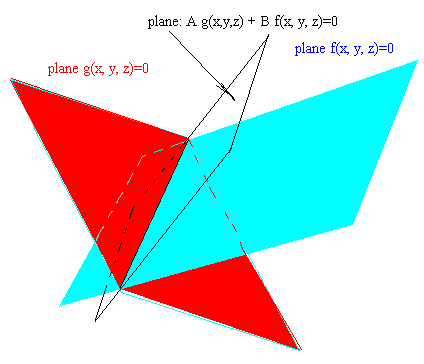
. Let A x
+ By +Cz +D=0 and
Let A x
+ By +Cz +D=0 and 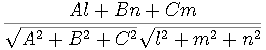 .
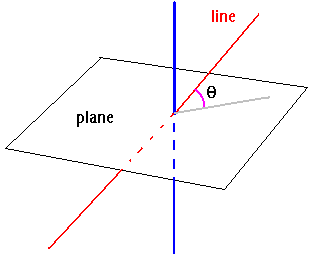
.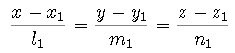 and
and 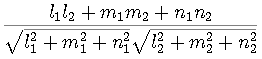 .
.
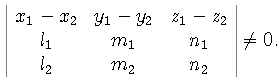
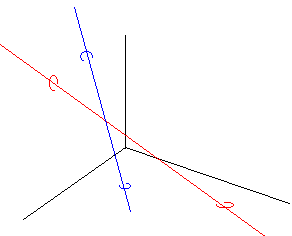
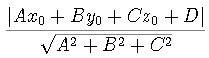 .
.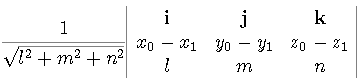 .
.
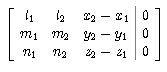 has a non-trivial solution ( t, -s, 1), i.e. D=det
has a non-trivial solution ( t, -s, 1), i.e. D=det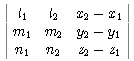 =0,
which is a necessary condition.
=0,
which is a necessary condition.